Building Optimization
This notebook performs building design optimization using EnergyPlus and BESOS helper functions. We load a model from in.idf, define parameters to vary, set objectives, test the model, then run a multi-objective genetic algorithm and plot the optimized designs.
Import libraries
import pandas as pd
from besos import eppy_funcs as ef, sampling
from besos.evaluator import EvaluatorEP
from besos.optimizer import NSGAII, df_solution_to_solutions
from besos.parameters import RangeParameter, expand_plist, wwr
from besos.problem import EPProblem
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from platypus import Archive, Hypervolume, Solution
Load the base EnergyPlus .idf file
building = ef.get_building("in.idf")
Define design parameters and ranges
Define a parameter list using a helper function, in this case building orientation and window-to-wall ratio.
parameters = []
parameters = expand_plist(
{"Building 1": {"North Axis": (0, 359)}} # Name from IDF Building object
)
parameters.append(
wwr(RangeParameter(0.1, 0.9))
) # Add window-to-wall ratio as a parameter between 0.1 and 0.9 using a custom function
Objectives
Using Heating and Cooling energy outputs as simulation objectives, make a problem instance from these parameters and objectives.
objectives = ["DistrictCooling:Facility", "DistrictHeating:Facility"]
besos_problem = EPProblem(parameters, objectives)
Set up EnergyPlus evaluator object to run simulations for this building and problem
evaluator = EvaluatorEP(
besos_problem, building, out_dir="outputdir", err_dir="outputdir"
) # outputdir must exist; E+ files will be written there
runs = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{"0": [180, 0.5]}, orient="index"
) # Make a dataframe of runs with one entry for South and 50% glazing
outputs = evaluator.df_apply(runs) # Run this as a test
outputs
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=0.0, description='Executing', max=1.0, style=ProgressStyle(description_widt…
| DistrictCooling:Facility | DistrictHeating:Facility | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.233564e+09 | 4.931726e+09 |
Run the Genetic Algorithm
Run the optimizer using this evaluator for a population size of 20 for 10 generations.
results = NSGAII(evaluator, evaluations=10, population_size=20)
results
| North Axis | RangeParameter [0.1, 0.9] | DistrictCooling:Facility | DistrictHeating:Facility | violation | pareto-optimal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 263.141621 | 0.129692 | 4.295335e+09 | 2.518508e+09 | 0 | True |
| 1 | 292.002451 | 0.227006 | 4.463966e+09 | 2.689957e+09 | 0 | False |
| 2 | 339.185394 | 0.683410 | 4.385552e+09 | 4.164144e+09 | 0 | False |
| 3 | 299.642312 | 0.305285 | 4.484553e+09 | 2.958204e+09 | 0 | False |
| 4 | 28.829169 | 0.280137 | 4.322465e+09 | 2.577191e+09 | 0 | False |
| 5 | 193.942624 | 0.632927 | 3.270069e+09 | 5.663412e+09 | 0 | True |
| 6 | 284.171269 | 0.423629 | 4.453051e+09 | 3.709380e+09 | 0 | False |
| 7 | 201.004448 | 0.205321 | 3.491288e+09 | 3.299567e+09 | 0 | True |
| 8 | 222.356347 | 0.838719 | 3.679302e+09 | 6.640699e+09 | 0 | False |
| 9 | 300.243976 | 0.727996 | 4.598198e+09 | 4.884347e+09 | 0 | False |
| 10 | 131.502074 | 0.272879 | 3.756134e+09 | 3.589675e+09 | 0 | False |
| 11 | 317.780853 | 0.243146 | 4.464903e+09 | 2.490665e+09 | 0 | True |
| 12 | 317.265378 | 0.642623 | 4.529079e+09 | 4.232315e+09 | 0 | False |
| 13 | 78.522690 | 0.536158 | 4.345231e+09 | 4.379867e+09 | 0 | False |
| 14 | 300.109981 | 0.594342 | 4.547690e+09 | 4.280460e+09 | 0 | False |
| 15 | 233.827874 | 0.249924 | 3.905637e+09 | 3.391033e+09 | 0 | False |
| 16 | 4.219275 | 0.607486 | 4.256356e+09 | 3.775692e+09 | 0 | False |
| 17 | 350.548384 | 0.494473 | 4.280642e+09 | 3.334591e+09 | 0 | False |
| 18 | 60.838750 | 0.874669 | 4.558749e+09 | 5.692981e+09 | 0 | False |
| 19 | 311.211108 | 0.498106 | 4.510503e+09 | 3.688458e+09 | 0 | False |
Visualize the results
optres = results.loc[
results["pareto-optimal"] == True, :
] # Get only the optimal results
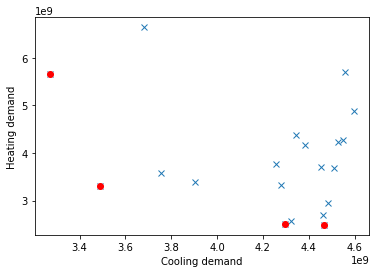
plt.plot(
results["DistrictCooling:Facility"], results["DistrictHeating:Facility"], "x"
) # Plot all results in the background as blue crosses
plt.plot(
optres["DistrictCooling:Facility"], optres["DistrictHeating:Facility"], "ro"
) # Plot optimal results in red
plt.xlabel("Cooling demand")
plt.ylabel("Heating demand")
Text(0, 0.5, 'Heating demand')
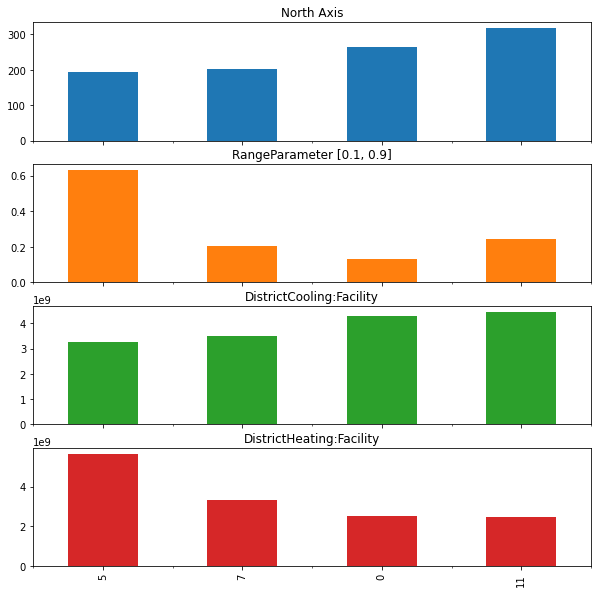
optres = optres.sort_values("DistrictCooling:Facility") # Sort by the first objective
optresplot = optres.drop(columns="violation") # Remove the constraint violation column
ax = optresplot.plot.bar(
subplots=True, legend=None, figsize=(10, 10)
) # Plot the variable values of each of the optimal solutions
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pandas/plotting/_matplotlib/tools.py:307: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The rowNum attribute was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.2 and will be removed two minor releases later. Use ax.get_subplotspec().rowspan.start instead.
layout[ax.rowNum, ax.colNum] = ax.get_visible()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pandas/plotting/_matplotlib/tools.py:307: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The colNum attribute was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.2 and will be removed two minor releases later. Use ax.get_subplotspec().colspan.start instead.
layout[ax.rowNum, ax.colNum] = ax.get_visible()
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pandas/plotting/_matplotlib/tools.py:313: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The rowNum attribute was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.2 and will be removed two minor releases later. Use ax.get_subplotspec().rowspan.start instead.
if not layout[ax.rowNum + 1, ax.colNum]:
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pandas/plotting/_matplotlib/tools.py:313: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The colNum attribute was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.2 and will be removed two minor releases later. Use ax.get_subplotspec().colspan.start instead.
if not layout[ax.rowNum + 1, ax.colNum]:
Hypervolume
Now that initial results have been produced and verified against expectations, enlarge evaluations and population size to produce increased optimization of results.
results_2 = NSGAII(evaluator, evaluations=20, population_size=50)
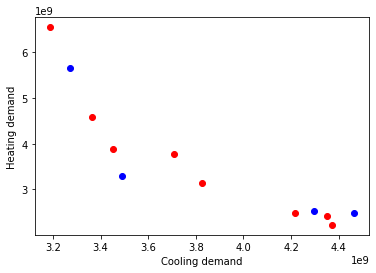
Compare first run and second run
optres_2 = results_2.loc[results_2["pareto-optimal"] == True, :]
plt.plot(
optres["DistrictCooling:Facility"], optres["DistrictHeating:Facility"], "bo"
) # Plot first optimal results in blue
plt.plot(
optres_2["DistrictCooling:Facility"], optres_2["DistrictHeating:Facility"], "ro"
) # Plot second optimal results in red
plt.xlabel("Cooling demand")
plt.ylabel("Heating demand")
Text(0, 0.5, 'Heating demand')
Calculate the hypervolume
reference_set = Archive()
platypus_problem = evaluator.to_platypus()
for _ in range(20):
solution = Solution(platypus_problem)
solution.variables = sampling.dist_sampler(
sampling.lhs, besos_problem, 1
).values.tolist()[0]
solution.evaluate()
reference_set.add(solution)
hyp = Hypervolume(reference_set)
print(
"Hypervolume for result 1:",
hyp.calculate(df_solution_to_solutions(results, platypus_problem, besos_problem)),
)
print(
"Hypervolume for result 2:",
hyp.calculate(df_solution_to_solutions(results_2, platypus_problem, besos_problem)),
)
Hypervolume for result 1: 0.27192093845955767
Hypervolume for result 2: 0.23978050252228306